American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists issuing body. To improve care during pregnancy labour and birth for women and their babies.

Executive Summary Of The 2020 Clinical Practice Guidelines For The Management Of Hypertension In The Philippines Ona 2021 The Journal Of Clinical Hypertension Wiley Online Library
Chronic hypertension in pregnancy is defined by the American College of Obstetrics and Gynecology ACOG as blood pressure 140 mm Hg systolic andor 90 mm Hg diastolic before pregnancy or in recognition that many women seek medical care only once pregnant before 20 weeks of gestation use of antihypertensive medications before.
. Drug-related and substance-related causes 2. Hypertension is the commonest medical disorder in pregnancy. Included were multi-disciplinary CPGs that were.
In Western Australia alone Hypertension occurs in 40 of all pregnancies 27 due to Pre-Eclampsia and 136 due to Essential Hypertension. Hypertensive emergency of pregnancy is classified as 1 acute increase in blood pressures greater than or equal to 160110 mm Hg 2 development of symptoms consistent with severe preeclampsia and 3 symptoms of end-organ damage. Chronic Hypertension in Pregnancy.
Prevention of hypertension in pregnancy PREVENTION OF HPN IN PREGNANCY Low dose aspirin recommended in reducing the risk of preeclampsia in patients who are moderate to high risk Dose 60-80mgday Calcium supplementation may prevent preeclampsia in patients with low dietary intake of calcium Dose 15-2g elemental. This guideline was partially updated in June 2019. Pre-existing hypertension pregnancy-induced hypertension and.
I published within the last 10 years 200313 and the then accepted 2014 SOGC guideline now published ii covered the diagnosis assessment and management of onemore of the HDPs in human pregnancy and iii were written in English French Dutch or German ie languages. Various types of hypertension affecting pregnancy are. The rate of maternal chronic hypertension increased by 67 from 2000 to 2009 with the largest increase 87 among African American women.
14 Although comparison of less tight. Chronic hypertension is present in 09-15 of pregnant women and may result in significant maternal fetal and neonatal morbidity and mortality. Creasy and Resniks 8th Ed.
SourceClinical Practice Guidelines. Care should always be individualized by adding patient. Methodology Principal Findings MEDLINE EMBASE Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials Cochrane.
The rate of maternal chronic hypertension increased by 67 from 2000 to 2009 with the largest increase 87 among African American women. Date Modified By Description 10 050316 20 Abbreviations HELLP Haemolysis Elevated Liver Enzymes and Low Platelets HDP Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy IUGR Intrauterine Growth Restriction. It is intended to be used with reference to the full version of.
Healthcare professionals Women who develop hypertension during pregnancy who have hypertension and wish to conceive and who have had a pregnancy complicated by hypertension and their relatives and carers. Read the Committee Opinion. This increase is largely secondary to the obesity.
100 1 100 found this document useful 1 vote 449 views 60 pages. CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE The Management of Hypertension in Pregnancy 4 10 Revision History Version No. PE is defined as hypertension blood pressure 14090 mmHg with organ damage that develops after 20 weeks of gestation and has the potential to result in serious adverse consequences for the mother and fetus.
24 of Perinatal Deaths are due to Hypertension in pregnancy3 4. Chronic kidney disease. The United Kingdom UK appears to have fallen hypertension in pregnancy remains one of the leading causes of maternal death in the UK2.
Severe-range hypertension is defined as blood pressure values exceeding 160110 mm Hg. We systematically reviewed existing CPGs on the HDPs hypertensive disorders of pregnancy to inform clinical practice. Save Save Hypertension in Pregnancy Pogs-cpg For Later.
On Hypertension for their tireless effort in coming up with this latest edition of the Hypertension Clinical Practice Guideline. This is the executive summary of the MOH Clinical Practice Guidelines CPG on Hypertension. 25 Identifiable secondary causes of hypertension 1.
Pre-existing hypertension affects 1 to 5 of pregnancies whereas Pregnancy Induced Hypertension occurs in 5 to 10 of all pregnancies. Quality MeasuresClinical Practice Guidelines Disclaimer. For the purpose of this guideline pregnancy includes the antenatal intrapartum and postpartum 6 weeks after birth periods.
First more aggressive treatment of hypertension in pregnancy prevents the development of severe hypertension as demonstrated by both a systematic review of randomized trials 152 and CHIPS Control of Hypertension in Pregnancy Study in which the average BP achieved by tight control was 13385 mm Hg. Task Force on Hypertension in Pregnancy author. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.
GH is hypertension that develops any time after 20 weeks of gestation without proteinuria. Hypertension in pregnancy developed by the Task Force on Hypertension in Pregnancy. This is the fifth in the series since it was first launched in 1998.
Clinical Practice Guidelines represent a consistentstandardized approach to the care of patients with specific diagnoses. Chronic hypertension is present in 0915 of pregnant women 1 and may result in significant maternal fetal and neonatal morbidity and mortality. Target organ damage can be manifested by.
Chronic hypertension is present in 0915 of pregnant women and may result in significant maternal fetal and neonatal morbidity and mortality. Background Clinical practice guidelines CPGs are developed to assist health care providers in decision-making. Table 3 Identifiable secondary causes of hypertension CPG pg.
Four Types of Hypertensive Disease 1. This reflects the rapid evolution of knowledge in hypertension driven by major outcome trials for which there were a few since the last edition 5. Hypertension defined as systolic blood pressure 140 mmHg or diastolic blood pressure 90 mmHg either pregnancy-related or chronic is a common complication of pregnancy.
Hypertension in Pregnancy Pogs-Cpg. This clinical guideline concerns the management of hypertensive disorders in pregnancy and their complications from preconception to the postnatal period. This increase is largely secondary to the.
Gestational hypertensionevidence for the preeclampsia syndrome does not develop and hypertension resolves by 12 weeks postpartum 2. Clinical Practice Guidelines Einc 2014. In Pregnancy Jhon Philip Fuego Clinical Clerk WVSU-Medical Center Hypertension Appropriately taken blood pressure exceeding 140 mm Hg systolic or 90 mm Hg diastolic.
When severe defined as systolic blood pressure 160 mmHg or diastolic blood pressure 110 mmHg it can lead to stroke and death but prompt. Who is it for.

Pdf Malaysia Cpg For Heart Failure

Pregnancy Induced Hypertension

Pregnancy Induced Hypertension

Pregnancy Induced Hypertension
Clinical Practice Guidelines Pogs Website

Executive Summary Of The 2020 Clinical Practice Guidelines For The Management Of Hypertension In The Philippines Ona 2021 The Journal Of Clinical Hypertension Wiley Online Library

Pregnancy Induced Hypertension

Pregnancy Induced Hypertension

Examples Of Scenarios Used During The Qualitative First Study And The Download Table
Plos One Hypertensive Disorders Of Pregnancy A Systematic Review Of International Clinical Practice Guidelines
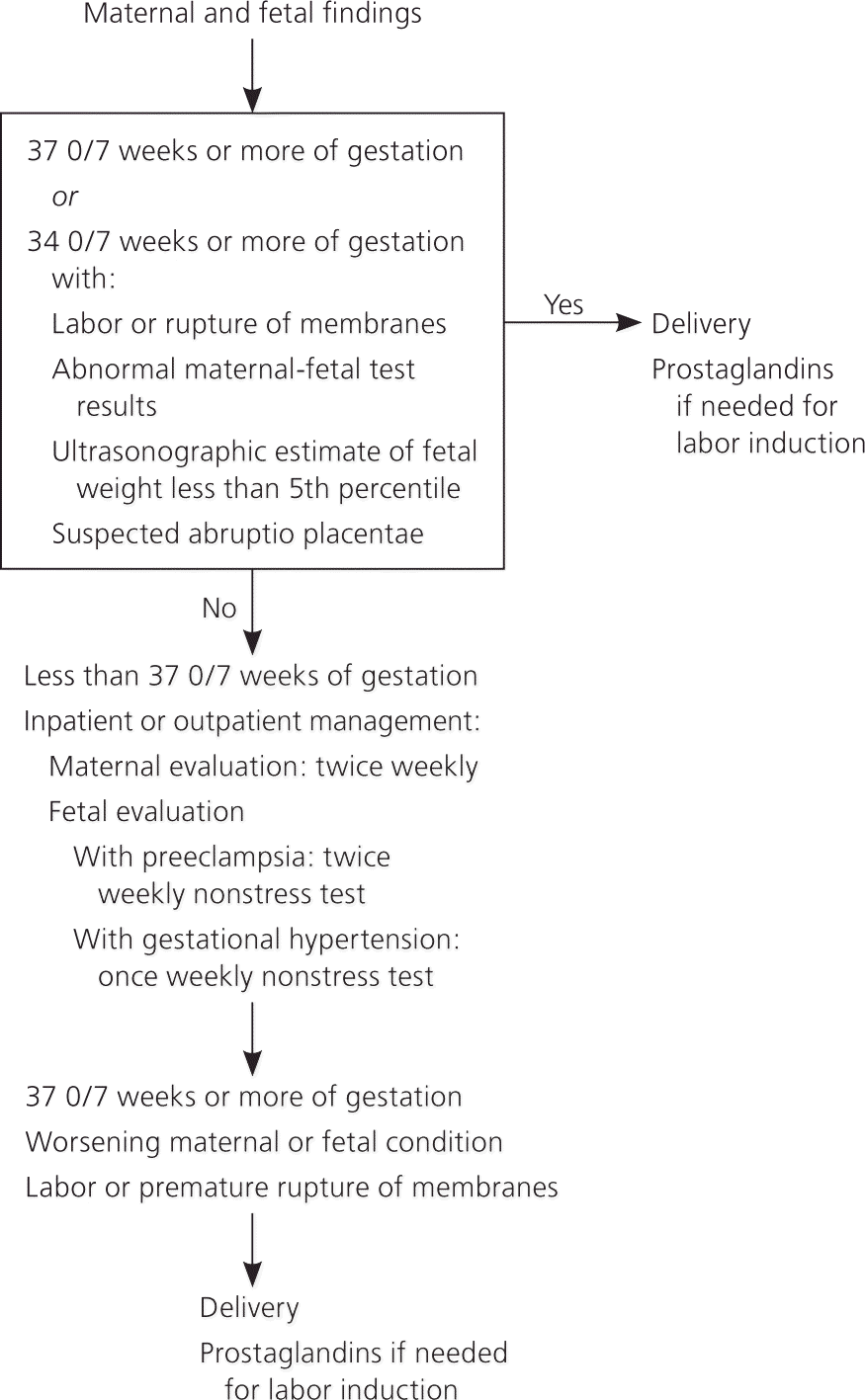
Hypertensive Disorders Of Pregnancy

Bahagian Pembangunan Kesihatan Keluarga Kesihatan Ibu
Clinical Practice Guidelines Pogs Website
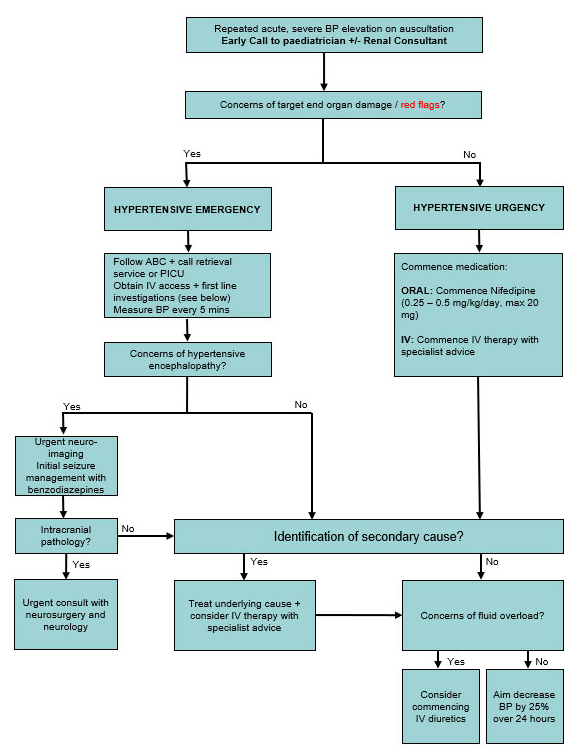
Clinical Practice Guidelines Hypertension In Children And Adolescents

Clinical Practice Guidelines Hypertension In Children And Adolescents

Executive Summary Of The 2020 Clinical Practice Guidelines For The Management Of Hypertension In The Philippines Ona 2021 The Journal Of Clinical Hypertension Wiley Online Library


